UMD CHEMISTRY GARDEN
Medical Molecules in Our Garden






Spring 2021


Rebekah and Joshua - planting Myrtensia, MIke, Alfonso, Bleriot

Class of Spring 2020

Solomon Kojo Attionu
- Hometown? Accra, Ghana
- How did you first get interested in Chemistry? After watching the videos "Chemical Curiosities" by Chris Bishop
- What challenge in the world do you hope we can address with chemistry? Develop new cancer therapeutics
- What is your favorite plant? Hydrangea
- What is your favorite food? Fufu and peanut butter soup

Nandina
Nandina domestica is a species of flowering plant in the family Berberidaceae. Commonly known as heavenly or sacred bamboo, it is native to eastern Asia, from the Himalayas to Japan. It is widely grown as an ornamental plant due to its colorful foliage. Higenamine is a plant-based alkaloid widely used as a nutritional supplement in food and beverage industries. It has a variety of biological activities such as inhibition of nitric oxide synthase, stimulation of cardiac ẞ-adrenoceptor and platelet anti-aggregation
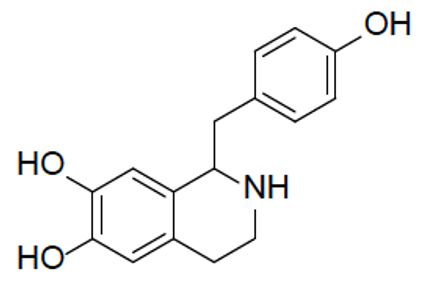
Higenamine from Nandina
Higenamine is a plant-based alkaloid widely used as a nutritional OH supplement by the food and beverage industries. It has a variety of biological activities such as inhibition of nitric oxide synthase, stimulation of cardiac ẞ-adrenoceptor and platelet anti-aggregation.

Vinca minor is a species of flowering plant in the dogbane family. It is a trailing subshrub commonly known as dwarf or lesser periwinkle. It is also known as creeping myrtle in the United States. It is native to central and southern Europe.
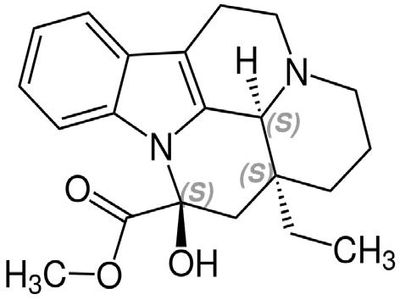
Vincamine from Vinca
Vincamine is a monoterpenoid indole alkaloid found in the leaves of Vinca minor. It is used for the treatment of degenerative and vascular dementia in Europe. In the United States, it is used as a dietary supplement.

Mona Abdelrahman
- Hometown? Cairo, Egypt
- How did you first get interested in Chemistry? Science has been my passion since a young age, and then I discovered that everything we do is Chemistry!
- What challenge in the world do you hope we can address with chemistry? The scarcity of water for many people.
- What is your favorite plant? The Birch tree
- What is your favorite food? Egyptian falafel with green salad

Rose Hips
Rose hips are referred to as Rosa canina pseudo fruits. They are aggregate fruits consisting of several achenes (the actual seed-containing fruits of rose hips) enclosed by an enlarged, red, fleshy floral cup (hypanthium). Rose hips have been used as herbal medicine for more than 2,000 years.
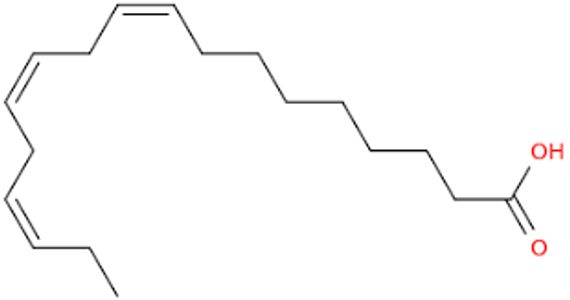
α- linolenic acid
Polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs): The seeds of R. canina fruits are rich in the ω-3 and ω-6 PUFAs; PUFAs decrease the concentration of triglycerides and cholesterol in the blood, inhibit thrombosis, help dilation of blood vessels, enhance blood fluidity, increase plasticity of erythrocytes, and inhibit
inflammation such as linoleic and α- linolenic acids.

River Birch
River birch tree belongs to the family Betulaceae. They are called the most beautiful American trees. Also known as red birch, water birch or black birch. River birch is perhaps the most culturally adaptable and heat tolerant of the birches.
Betulinic acid from Birch
Betulinic acid is present in considerable amounts in the outer bark of a variety of tree species, e.g. birch trees. Betulinic acid has a number of biological activities, particularly the antitumor activity. It has the ability to trigger the mitochondrial pathway of apoptosis in cancer cells.

Cassie Youshaw
- Hometown: Howard County, MD. USA
- How did you first get interested in Chemistry? Organic chemistry was my favorite class, I was amazed at the amount of possibilities you could do with it.
- What is one the world's biggest challenges that you hope we can address by a better understanding of chemistry? Plastic waste
- What is your favorite plant? Snake Plants
- What is your favorite food? Cheeseburgers

Daffodil
Daffodil is in the plant family Amaryllidaceae and the genus
Narcissus. It is a spring flowering perennial that grows from a bulb, the flowers are usually white or yellow in color.
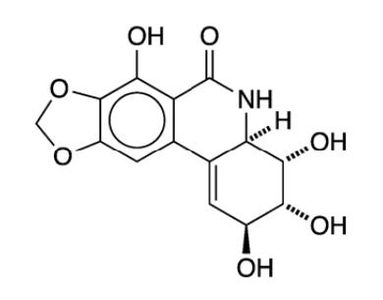
Narciclasine
Narciclasine has a long history of medicinal properties dating back to 460-370 B.C. when Hippokrates of Kos used narcissus oil to treat tumors. This compound has potent biological activity, and its derivatives have been studied as anticancer agents. The fused rings in narciclasine make the molecule unique, and the abundant functional groups make the molecule attractive for synthetic purposes .

Hellebore
Hellebore is a perennial herb in the family Ranunculaceae. All parts of this plant are toxic due to the alkaloids contained in the plant and it is depicted throughout history and folklore as a poison.

Ranunculin
Ranunculin is a glycoside, prone to acid-catalyzed hydrolysis and when Hellebore is injured, it undergoes enzymatic cleavage and dehydration to produce protoanemonin, a poison.

Edward Chinn
- Hometown? New Carrolton, MD., USA
- How did you first get interested in Chemistry? I had an excellent Organic Chemistry Professor, Sripriya Seetharaman, who inspired me to believe that I could be a great chemist.
- What challenge in the world do you hope we can address with chemistry? Finding solutions to antibiotic resistant pathogens
- What is your favorite plant? Cherry Tree
- What is your favorite food? Tacos with everything imaginable on them, except hot sauce

Beautyberry
Callicarpa americana is a flowering bush in the Verbena Family. C. americana is also called American Beautyberry and is commonly found in the southern and eastern United States. Folklore says that the crushed leaves of American Beautyberry bushes have insect repellant properties.
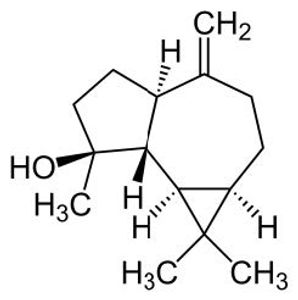
(+)-Spathulenol
(+)-Spathulenol is one of the compounds in the
leaves of American Beautyberry, which is known to have insect repellant properties. The structure of (+)-spathulenol has 5 chiral centers and, in one study, the compound was shown to reduce the percentage of mosquitoes that bite by over 30%, making it better than the common repellant DEET.

Ginkgo biloba
Ginkgo biloba is native to Asia and is one of the oldest living organisms alive today. Fossils of Ginkgo biloba have been found to be 270 million years old, and the plant has been referred to as a living fossil. It has been used for generations in Chinese folk medicine for improving and preventing mental decline.

Ginkgolide
Ginkgolide B is a highly functionalized molecule. It has 6 fused ring structures, which give it a rigid conformation. Ginkgolide B is a platelet-activating factor antagonist that has neuroprotective properties and is one of the active species in Ginkgo biloba.

Allison Keyes
- Hometown? Olney, MD, USA
- How did you first get interested in Chemistry? I enjoyed Dr. Montague-Smith's course and Dr. Davis' research group; they made organic chemistry exciting and relevant to my career in dentistry.
- What challenge in the world do you hope we can address with chemistry? Reducing hunger
- What is your favorite plant? Chlorophytum comosum (spider plant)
- What is your favorite food? Cupcakes & chicken parmigiana

Hydrangea
Hydrangea is a flowering plant in the family Hydrangeaceae, which is native to Japan. The petals and sepals of these flowers vary in color depending on pH. In general, blue hydrangea exists in more acidic soil whereas red/pink hydrangea exists in more alkaline soil.
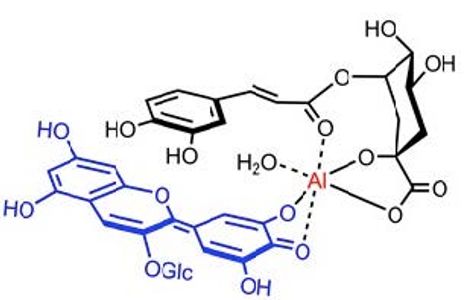
Metalloanthocyanin
Hydrangea-Blue Complex is a metalloanthocyanin, which has been proposed to give rise to the blue petal and sepal color in Hydrangea. This complex involves aluminum ions and anthocyanin.

Winterberry
Winterberry, (Ilex verticillata) is a shrub and species of holly in the family Aquifoliaceae, which is native to eastern North America. The petals and sepals of these flowers can range from purple and blue. Its red berries are a food source for wildlife.
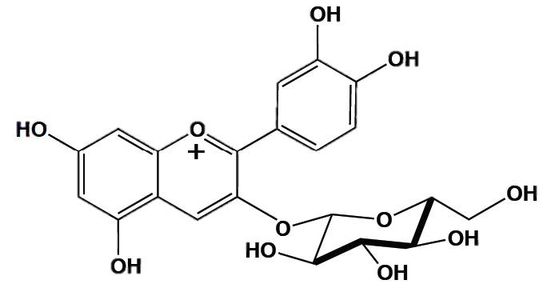
Anthocyanin
Anthocyanins are water-soluble vascular flavonoid pigments that vary in color. Depending on pH, the compound may look purple, pink, or blue. Flavonoids are anti- oxidants. Potential applications include natural food colorants and textile dyes.
Laura Kuperman
- Hometown? Ponte Vedra Beach, FL, USA
- How did you first get interested in Chemistry? In high school I completed an independent research project examining the effects of bisphenol A (BPA) on fruit flies
- What challenge in the world do you hope we can address with chemistry? Removal of man-made toxins from the environment.
- What is your favorite plant? Laurel tree
- What is your favorite food? Korean short ribs

Barberry
Barberry (Berberis sp.) is a deciduous, evergreen shrub that produces tart, red berries. The berries are commonly used for culinary purposes across Europe, the Middle East, and Central Asia. It has also been used for medicinal purposes in China for centuries.
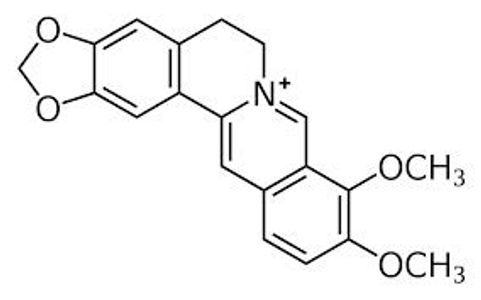
Berberine
Berberine is an isoquinoline alkaloid produced by barberry, as well as some plants in the buttercup family Ranunculaceae (tree turmeric, Oregon grape, and so on). This compound and its derivatives exhibit antibacterial activities by interfering in cellular division of bacteria to prevent their spread.

Rhododendron
Rhododendron and other similar plants, such as azalea, are flowering shrubs native to Asia, but are also common in the United States. They belong to the family Ericaceae, plants of which tend to sprout in acidic and infertile growing conditions.

Grayanotoxin
Grayanotoxin refers to a class of toxic diterpenoids produced by plants of the Ericaceae family. Honey made from rhododendron and azalea flowers typically contains this toxin and is called “Mad Honey” for its maddening effects on humans and animals. Grayanotoxin prevents inactivation of sodium channels, and has been used as a pharmacological tool to improve knowledge about the workings of sodium channels.
Suvenika Perera
- Hometown? Colombo, Sri Lanka
- How did you first get interested in Chemistry? My chemistry practical class in school, it made me interested in chemistry.
- What challenge in the world do you hope we can address with chemistry? A solution to environmental pollution
- What is your favorite plant? Rose
- What is your favorite food? Cashew curry

Juniper
Juniper belongs to the genus, Juniperus of the cypress family Cupressaceae. This is an evergreen tree that produces berries, mostly blue in color. Juniper berries are used as spice and to make an essential oil.
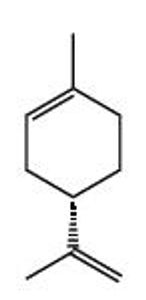
Limonene
Limonene is a cyclic monoterpene and is the major constituent in the oil of citrus peel. Limonene is a major component in a wide variety of plants such as juniper, cottonwoods, spruce, the list goes on. Limonene is used extensively in the food and perfume industries.

Prunus
Prunus is an evergreen tree that belongs to the rose family Rosaceae. Flowers are usually white to pink. This plant is native to northern temperate regions.

Chlorogenic acid
Chlorogenic acid naturally occurs in prunus, coffee beans, eggplant, etc. The catechol moiety in this natural product enables radical scavenging activity. Antibacterial and antitumor activities are also prominent biological activities of this compound.
The Instructors

Jeffery Davis
Paul Paukstelis
Andrea Ottesen
- Hometown? Williamston, MA, USA
- How did you first get interested in Chemistry? I was a bio major until I studied organic chemistry with a dynamic teacher, Prof. Tom Newton at Colby College
- What challenge in the world do you hope we can address with chemistry? At the present, developing new anti-viral agents
- What is your favorite plant? Sugar
- Hometown? Williamston, MA, USA
- How did you first get interested in Chemistry? I was a bio major until I studied organic chemistry with a dynamic teacher, Prof. Tom Newton at Colby College
- What challenge in the world do you hope we can address with chemistry? At the present, developing new anti-viral agents
- What is your favorite plant? Sugar Maple
- What is your favorite food? It's a toss-up between Portuguese Kale Soup or a smoking hot vindaloo

Andrea Ottesen
Paul Paukstelis
Andrea Ottesen
- Hometown? DC and Maryland Suburbs
- How did you first get interested in Chemistry? I got passionate about chemistry when I started working with Dr. Jim Duke at his GreenPharmacy Medicinal Plant Garden.
- What challenge in the world do you hope we can address with chemistry? Natural resource and ecosystem conservation integrated with production
- Hometown? DC and Maryland Suburbs
- How did you first get interested in Chemistry? I got passionate about chemistry when I started working with Dr. Jim Duke at his GreenPharmacy Medicinal Plant Garden.
- What challenge in the world do you hope we can address with chemistry? Natural resource and ecosystem conservation integrated with production of healthy food and medicine for improved public health stewardship.
- What is your favorite plant? Arisaema spp.
- What is your favorite food? Tikka Masala

Paul Paukstelis
Paul Paukstelis
Paul Paukstelis
- Hometown? Manhattan, KS
- How did you first get interested in Chemistry? Both of my parents were chemists, so naturally I studied Biology instead. It took some time, but it became clear that biology is just chemistry if you start to ask the hard questions.
- What challenge in the world do you hope we can address with chemistry? Clean/renewabl
- Hometown? Manhattan, KS
- How did you first get interested in Chemistry? Both of my parents were chemists, so naturally I studied Biology instead. It took some time, but it became clear that biology is just chemistry if you start to ask the hard questions.
- What challenge in the world do you hope we can address with chemistry? Clean/renewable energy.
- What is your favorite plant? Any of the prairie grasses (big bluestem, Indian grass, cordgrass).
- What is your favorite food? Sour cream